Rutin is a flavonoid, a type of plant pigment that has antioxidant properties. It is found in various fruits, vegetables, and plants
Rutin
SYNONYMS: Rutocide
SPEC.:NF11 DAB EP
TEST METHOD: UV
PLANT SOURCE:Scphora japonica L.
CAS NO:153-18-4
MOLECULAR FORMULA & MOLECULAR Mass:C27H30O16 610.52
STRUCTURAL FORMULA:
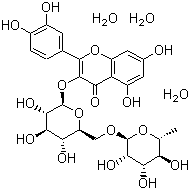
CHARACTERISTIC:
Rutin: Yellow or yellow-green powder or very fine needle-like crystal, odorless, tasteless, in the air gradually becomes darker, heated to 185-192 c into a jelly-brown. Difficult to dissolve in cold water (0.0013%), soluble in hot water (0.55%), hot methanol (11.2%), cold methanol (1.0%), hot ethanol (3.5 percent), cold ethanol (0.36%) cold pyridine (8.5 %), soluble in alkaline, and acid precipitation. Insoluble in other organic solvents.
PHARMACOLOGY: Rutin, the glycoside form of quercetin, is a bioflavonoid having an aromatic trimeric heterocyclic structure. It is a naturally occurring pigment. It, chemically 3-[[6-o-(6-deoxy-alpha-l-mannopyranosyl)-beta-d-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) -5,7-dihydroxy-4h-1-benzopyran-4-one, is a yellow to greenish crystalline powder melting at 190 c. Rutin is classified as vitamin P which increases the strength of the walls of the blood capillaries and regulates their permeability. Others classified as vitamin P are catechin, citrin, eriodictin, hesperetin, hesperidin, nobiletin, quercetin, sinensetin, and tangerine. It is not a dietary essential but is known to affect capillary disorders. It may also have a contribution to the total antioxidant activity and detoxifiers. It is also known to have pharmacological action as an anti-inflammatory, antihistaminic, and antiviral agent.
CHEMICAL ANALYSIS:
| ITEMS | RESULTS |
| Assay (anhydrous substance) | 95%—101.5% |
| Loss on drying | 5.5-9.0% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.5% |
| Impurity Quercetin | ≤5% |
| Chlorophyll | ≤0.004% |
| Red pigments | ≤0.004% |
| Heavy Metal | ≤20ppm |
| Mesh Size | 95% pass 80 mesh |









